

2019-09-09 20:38:00 Mon ET
federal reserve monetary policy treasury dollar employment inflation interest rate exchange rate macrofinance recession systemic risk economic growth central bank fomc greenback forward guidance euro capital global financial cycle credit cycle yield curve
Harvard macrofinance professor Robert Barro sees no good reasons for the recent sudden reversal of U.S. monetary policy normalization. As Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell yields to the persistent demands of a vocal president, the FOMC approves an interim interest rate cut by quarter point to 2%-2.25%. This rate cut represents a clear departure from the current business cycle of interest rate hikes in recent years. Barro advocates the Taylor monetary policy rule that the nominal interest rate should rise in response to higher inflation and economic output both relative to their targets. In accordance with the key Taylor monetary policy rule, the nominal interest rate normally tends toward a gradual long-term equilibrium path.
In this light, Barro regards the recent interest rate reduction as a special deviation from the prior path of U.S. monetary policy normalization. Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell seems to justify the recent interest rate cut in terms of the fact that U.S. inflation remains low and tame as the economy operates near full employment despite continual trade escalation between the U.S. and China. Barro indicates the clear and present danger that the recent rate reduction represents a dovish Powell response to many stock market analysts and the Trump administration.
If any of our AYA Analytica financial health memos (FHM), blog posts, ebooks, newsletters, and notifications etc, or any other form of online content curation, involves potential copyright concerns, please feel free to contact us at service@ayafintech.network so that we can remove relevant content in response to any such request within a reasonable time frame.
2019-11-21 11:34:00 Thursday ET

Berkeley macro economist Brad DeLong sees no good reasons for an imminent economic recession with mass unemployment and even depression. The current U.S. ec
2017-04-01 06:40:00 Saturday ET
With the current interest rate hike, large banks and insurance companies are likely to benefit from higher equity risk premiums and interest rate spreads.
2026-04-30 08:28:00 Thursday ET

In the current global market for better biotech advances, medical innovations, and healthcare services, the new integration of artificial intelligence (AI)
2019-08-30 11:35:00 Friday ET

The conventional wisdom suggests that chameleons change their skin coloration to camouflage their presence for survival through Darwinian biological evoluti
2017-12-19 09:39:00 Tuesday ET
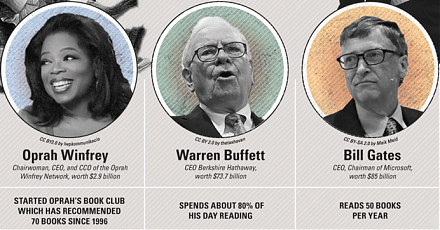
From Oprah Winfrey to Bill Gates, this infographic visualization summarizes the key habits and investment styles of highly successful entrepreneurs:
2018-01-13 08:39:00 Saturday ET

The Economist digs deep into the political economy of U.S. government shutdown over 3 days in January 2018. In more than 4 years since 2014, U.S. government