

2018-09-01 07:34:00 Sat ET
technology social safety nets education infrastructure health insurance health care medical care medication vaccine social security pension deposit insurance
As the French economist who studies global economic inequality in his recent book *Capital in the New Century*, Thomas Piketty co-authors with John Bates Clark medal winner and Berkeley professor Emmanuel Saez the latest September 2018 World Inequality Report. This fresh report empirically demonstrates that the rise of income-and-wealth for the top 1% U.S. population mirrors the fall of income-and-wealth for the bottom 50% U.S. population. Specifically, the top 1% cohort rakes in more than 20% of U.S. national income in 2017 in comparison to only 11% back in 1980. At the same time, the bottom 50% cohort receives 12% of U.S. national income in 2017 in comparison to about 20% back in 1980.
Not only do the rich become richer and the poor become poorer, the income and wealth transfers seem simultaneous, synchronous, and causal in time-series data. This stark feature shows an empirically robust increase in U.S. economic inequality over the recent decades.
However, this socioeconomic issue cannot reflect talent concentration in specific labor markets. At least some of this dichotomous wealth inequality arises from the fact that several industries such as biotech, telecom, and social media mold large players with competitive moats into quasi-monopolies. These mega players invest heavily in patents, trademarks, copyrights, and other intellectual properties in order to safeguard their market dominance against external competitive forces.
Nobel Laureate and former chief economist at World Bank Joseph Stiglitz points out that tech titans have become quasi-monopolies with high market concentration. This concentration serves as a primary explanation for worse income and wealth inequality in America. When the network platform orchestrators such as Facebook, Apple, Microsoft, Google, Amazon, Netflix, and Twitter (FAMGANT) reinforce their market strength and dominance, they may violate antitrust laws and regulations. Also, several other industries such as pharmaceutical firms (Johnson & Johnson, Merck, and Pfizer etc) and telecoms (AT&T, Verizon, Sprint, and T-Mobile) are new additions to the checklist of U.S. quasi-monopolies.
This new technological trend aggravates socioeconomic inequality, deepens anti-competitive concerns, and harms consumer benefits in terms of longer-term price and quality improvements.
If any of our AYA Analytica financial health memos (FHM), blog posts, ebooks, newsletters, and notifications etc, or any other form of online content curation, involves potential copyright concerns, please feel free to contact us at service@ayafintech.network so that we can remove relevant content in response to any such request within a reasonable time frame.
2018-08-11 14:35:00 Saturday ET

The Trump administration imposes 20%-50% tariffs on Turkish imports due to a recent spat over the detention of an American pastor, Andrew Brunson, in Turkey
2021-02-02 14:24:00 Tuesday ET
Our proprietary alpha investment model outperforms the major stock market benchmarks such as S&P 500, MSCI, Dow Jones, and Nasdaq. We implement
2017-04-25 06:35:00 Tuesday ET
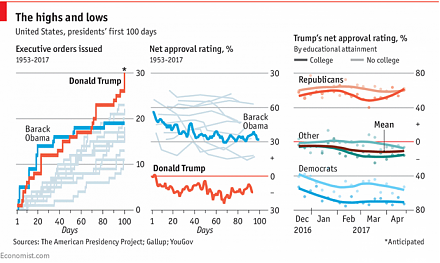
This nice and clear infographic visualization helps us better decipher the main memes and themes of President Donald Trump's first 100 days in office.
2018-01-07 09:33:00 Sunday ET

Zuckerberg announces his major changes in Facebook's newsfeed algorithm and user authentication. Facebook now has to change the newsfeed filter to prior
2022-02-15 14:41:00 Tuesday ET

Modern themes and insights in behavioral finance Lee, C.M., Shleifer, A., and Thaler, R.H. (1990). Anomalies: closed-end mutual funds. Journal
2021-08-01 07:26:00 Sunday ET

The Biden administration launches economic reforms in fiscal and monetary stimulus, global trade, finance, and technology. President Joe Biden proposes s