

2018-06-01 07:30:00 Fri ET
treasury deficit debt employment inflation interest rate macrofinance fiscal stimulus economic growth fiscal budget public finance treasury bond treasury yield sovereign debt sovereign wealth fund tax cuts government expenditures
The U.S. federal government debt has risen from less than 40% of total GDP about a decade ago to 78% as of May 2018. The Congressional Budget Office predicts that this ratio will surge to 96% in 2028. Although many blame the Trump tax cuts as the key root cause, the increases in health care and retirement benefits suggest a different real reason for U.S. deficit severity.
Harvard professor Martin Feldstein attributes the recent rise of U.S. budget deficit from 4% to 5% of total GDP to increases in Medicare and social security retirement benefits for middle-class older Americans. These increases in core health care and retirement benefits account for about 2.7% of total GDP. The neoclassical Sargent-Wallace thesis suggests that the central bank cannot finance incessant increases in core deficits with government bond issuance regardless of money supply growth. This money supply expansion would lead to inexorable inflationary pressures that defeat the dual mandate of both maximum employment and price stability in the suboptimal fiscal-monetary policy coordination. Inflation serves as a seigniorage tax that would in turn dampen real macroeconomic variates such as household consumption, capital investment, labor supply, and total economic output. In light of this ripple effect on sustainable financial market growth and prosperity, the law of inadvertent consequences counsels caution.
If any of our AYA Analytica financial health memos (FHM), blog posts, ebooks, newsletters, and notifications etc, or any other form of online content curation, involves potential copyright concerns, please feel free to contact us at service@ayafintech.network so that we can remove relevant content in response to any such request within a reasonable time frame.
2017-10-09 09:34:00 Monday ET
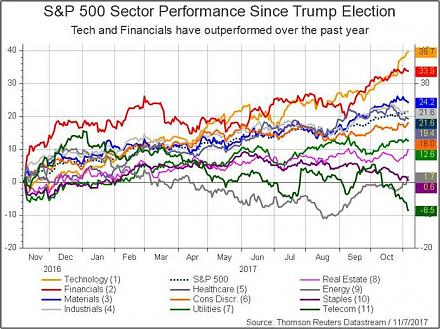
The current Trump stock market rally has been impressive from November 2016 to October 2017. S&P 500 has risen by 21.1% since the 2016 presidential elec
2017-10-27 06:35:00 Friday ET

Leon Cooperman, Chairman and CEO of Omega Advisors, points out that the current Trump stock market rally now approaches normalization. The U.S. stock market
2017-07-13 08:35:00 Thursday ET

President Donald Trump has announced that a major Apple iPhone upstream supplier, Foxconn Technology Group (aka Hon Hai Precision Group), will invest $10 bi
2018-04-02 07:33:00 Monday ET

China President Xi JinPing tries to ease trade tension between America and China in his presidential address at the annual Boao forum. In his vulnerable att
2018-03-27 07:33:00 Tuesday ET

CNBC's business anchorwoman Becky Quick interviews Nobel Laureate Joseph Stiglitz on the current trade war between America and China. As America imposes
2018-01-19 11:32:00 Friday ET

Most major economies grow with great synchronicity several years after the global financial crisis. These economies experience high stock market valuation,